Pool Cues vs Carom Cues: Understanding the Differences
Key Takeaways
- Carom cues are designed for precision-based games like three-cushion billiards. They are typically lighter, use smaller tips, and have stiffer tapers to provide the control, accuracy, and feedback needed for delicate rebounds and angled shots.
- Pool cues are built for pocket games such as 8-ball and 9-ball, where versatility and power are essential. With larger tips, heavier weight, and more flexible tapers, they can handle powerful breaks, spins, and a wide range of shot types.
- The key difference between carom cues and pool cues lies in their purpose: pool cues balance power and spin to pocket balls effectively, while carom cues prioritize finesse and stability to master rebounds, cushions, and precision shot-making on pocketless tables.
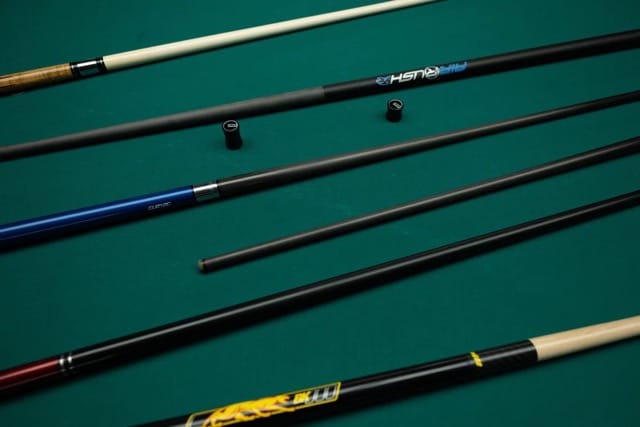

Pool Cues vs Carom Cues
Don’t settle for less, choose Pearson® Cues.
Our cues blend traditional inlaid design with modern innovation, creating tools that honor the past while shaping the future of the game. Play with Pearson® Cues and experience the perfect balance of heritage and progress.
What Is A Carom Cue?
Carom billiards is a family of cue sports, including straight rail, balkline, and three-cushion billiards, played on a table without pockets.
Instead of sinking balls, the goal is to strike the cue ball so it contacts both the opponent’s cue ball and at least one object ball, often rebounding off multiple cushions in the process. This makes the game all about precision, angles, and control, rather than power shots.
To meet these unique demands, carom cues are built differently from pool cues. A carom cue is designed to deliver finesse and accuracy, giving players the feedback and control they need to master rebounds and spins.

Carom cue. Source: LONGONI CAROM CUES – CALIFORNIA BILLIARDS
Specifications of Carom Billiard Cues
- Weight – Lighter than most pool cues, usually 470–510 grams (16.5–18 oz), allowing players to make subtle, controlled shots.
- Tip Size – Smaller than a pool cue, typically 11–12 mm, giving finer contact with the cue ball for accurate spins and deflections.
- Shaft Taper – Uses a straight or “European” taper, which provides a consistent, rigid feel ideal for precise control.
- Ferrule – Generally shorter than in pool cues, offering more feedback and sensitivity when striking the ball.
- Joint – Often made of wood for a smoother connection and slightly rearward balance, which helps with delicate cue ball control.
- Length – Similar to a pool cue, but with adjustments in weight and balance to suit carom play.
- Build & Finish – Commonly crafted from hardwoods, with high attention to straightness, smooth finish, and overall balance.
What Is A Pool Cue?
A pool cue is the most familiar type of cue, designed for cue sports like 8-ball, 9-ball, and snooker variants of pool.
A pool cue is a long, tapering rod, traditionally crafted from maple or ash but now also available in carbon fiber or fiberglass, that players use to strike the cue ball. There are 3 main types of pool cues:
- Standard Playing Cues – All-purpose cues used for most shots in games like 8-ball and 9-ball.
- Break Cues – Heavier and sturdier, designed to deliver maximum power to scatter balls at the start of the game.
- Jump Cues – Shorter and lighter, built for executing controlled shots that require the cue ball to hop over obstacles.
Depending on the game and playing style, pool cues vary in length, weight, and tip size, and different models exist for breaking, jumping, and regular play.

Pool cue
Read more: 5 Best Pool Cues For The Money (2025 Buyer’s Guide)
Specifications of Pool Cues
- Shaft – The top section that tapers toward the tip, usually made from hard maple or ash for strength and control.
- Tip – Typically leather (soft, medium, or hard), around 13 mm for American cues and 9–11 mm for British cues, chosen based on the size of balls and playing surface.
- Ferrule – A sleeve under the tip; plastic on American cues to handle heavy balls and powerful shots, brass on British cues for added precision.
- Butt – The thicker lower half of the cue, often with a wrap or grip, and housing the joint in two-piece cues.
- Length & Weight – Standard pool cues are about 57–59 inches long, weighing between 18–21 oz, allowing a balance of power and control.
- Material – Traditionally hardwood, but many modern cues feature carbon fiber or fiberglass for durability and low deflection.
Read more: How To Choose The Perfect Pool Cue Length? Tips To Pick Pool Cue Size
Also, the pool cue specifications can be varied based on the country, most popular are:
- American Cues – Larger 13 mm tips with plastic ferrules, ideal for striking bigger, heavier cue balls on faster cloths.
- British Cues – Smaller 9–11 mm tips with brass ferrules, built for precision on smaller tables with lighter cue balls, rewarding finesse and accuracy.
Carom Cues vs Pool Cues: The Unique Differences
At first glance, a pool cue and a carom cue might look like close cousins. They share the same basic shape, materials, and even length. Yet when you dive deeper, the differences are significant, and they exist because the games they are built for couldn’t be more different.
Pool cues are designed for pocket billiards games like 8-ball, 9-ball, and 10-ball. In these games, the aim is to strike the cue ball into object balls and sink them into pockets. This requires a balance of power for breaking racks, spin for controlling cue ball position, and versatility for different shot types.
By contrast, carom cues are engineered for games like three-cushion billiards, balkline, and straight rail, which fall under the family of carom billiards. These games are played on tables without pockets. Instead of sinking balls, the goal is to strike the cue ball so that it hits the other two balls, often rebounding off multiple cushions. Success in carom depends on precision, control, angles, and spin, rather than raw power.
Let’s break it down in detail:
Length and Weight Comparison
Pool cues are typically 58 inches long and weigh between 17 to 21 ounces. This size and weight combination helps players make powerful and accurate shots, particularly during break shots and when applying heavy spin.
Carom cues, in contrast, are often the same length but significantly lighter, usually ranging from 16.5 to 18 ounces. The lighter weight of carom billiard cues supports the precise and controlled shots needed in carom billiards, where finesse trumps power.
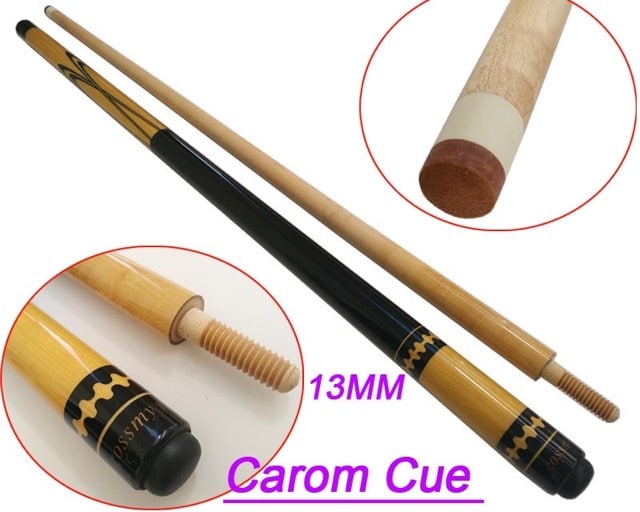

Carom cue usually shares the same length as pool cue, just lighter. Source: Reddit
Read more: What are the Optimal Pool Cue Weights?
Tip Size and Material Differences
The tip comparison reveals one of the most significant differences between these cue types:
Pool cue tips are wider, measuring around 12 to 13 millimeters in diameter. This larger tip size is designed for the various shots and spins required in pool games. Pool cue tips are usually made of leather, which grips the ball well for applying English and handling the heavier pool balls.
Carom cues feature narrower tips, measuring about 11 to 12 millimeters in diameter. This smaller tip size gives players the precision needed for the intricate shots of carom billiards. For reference, snooker cues have even smaller tips than carom cues (9-11mm diameter), showing the progression toward precision-focused games.
Read more: Unlock Your Pool Game: The Pool Cue Tip Hardness Chart
Construction and Taper Comparison
Carom cues are typically constructed with a stiffer conical taper compared to pool cues. This stiff taper is specifically needed to handle the larger, heavier carom balls effectively. The construction difference affects how energy transfers from the cue to the ball during impact.
Pool cues offer a more flexible taper design, providing a balance between stiffness and flexibility that accommodates the varied shot requirements in pool games.

Carom cue taper. Source: Fado
Material Variations
Both types of cues traditionally use maple wood, but carom cues sometimes incorporate ash wood instead of maple, which provides a different stiffness and feel compared to traditional pool cues. This material choice affects the cue’s responsiveness and feedback during play.
Joint Design and Feel
The joint construction differs between the two cue types, affecting the feel and feedback from each hit. Pool cues often feature metal pins in their joints, though some maintain wood-to-wood contact for a more traditional feel. The use of metal in the joint affects the cue’s balance point.
Carom billiard cues prioritize consistent feedback and are often designed with joints that provide the precise feel needed for the tactical shot-making in carom games.
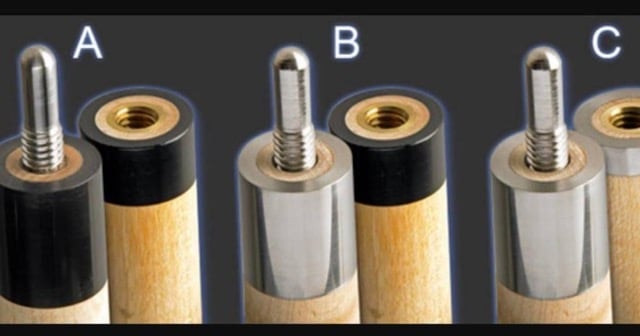
Pool cue offers different joint types. Source: Pearson Cues
Read more: 3 Pool Cue Joint Types (2025 Comprehensive Listing)
Design Philosophy: Power vs. Precision
Pool cues are engineered to offer a combination of power and precision, suitable for the varied shots in pool games. They must be robust enough to withstand the impact of powerful break shots while maintaining the control needed for delicate positioning plays.
Carom cues, with their focus on accuracy and finesse, are crafted specifically for the game’s precise hit patterns. They’re designed to aid in the control necessary for carom billiards’ more tactical and strategic shot-making approach.
Flexibility and Response Characteristics
Pool cues provide a balance between stiffness and flexibility, giving players consistent response across a wide range of shot types. This versatility allows players to execute everything from powerful breaks to subtle spin shots.
Carom cues favor a stiffer construction that provides the precise feedback needed for the game’s delicate shots. The reduced flexibility ensures that energy transfer is direct and predictable, crucial for the accuracy demanded in carom billiards.
Read more: How To Play Pool In 5 Steps? Beginners Guide To Playing Pool
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What is the difference between carom and billiard?
“Billiards” is the general name for cue sports, which includes both pool and carom. Carom billiards is a type of billiards played on a table without pockets, where the goal is to make the cue ball hit both object balls (and often cushions) to score points. Pool, another type of billiards, is played on a table with pockets, where the main objective is to sink balls into those pockets.
2. Is carom the same as pool?
No, carom is not the same as pool. Carom billiards uses pocketless tables and focuses on rebounds, angles, and cue ball control. Pool uses pocketed tables and focuses on sinking balls into the pockets.
3. Is carom harder than pool?
It depends on the player, but many consider carom harder than pool because there are no pockets. Scoring requires the cue ball to contact both object balls, often after hitting one or more cushions. This demands precise calculation of angles, spin, and speed.

Dave Pearson
Dave Pearson, the world's leading pool entertainer, is renowned globally as the ultimate exhibition player.
Boasting 20 world records endorsed by the prestigious Guinness Book of World Records, Dave established a legendary history in the sport industry.
